🎧 Listen to: Blood Transfusion
Blood Transfusion
Introduction: Why blood transfusion is important?
Blood is life! It carries oxygen and nutrients to every part of your body, keeping you strong and active. The average adult has about 5 to 6 liters of blood, which is about 10 to 12 sachets of water. But what happens if you lose a lot of blood due to an accident, surgery, or illness? That’s where blood transfusion comes in, a simple but life-saving process where blood from a healthy person (donor) is given to someone who needs it.
In Africa, millions of people need blood transfusions every year, but unfortunately, there is always a shortage of blood in hospitals. Many accident victims, pregnant women facing childbirth complications, and children with severe malaria or anaemia die because they don’t get blood in time. That’s why understanding blood transfusion is important for everyone.
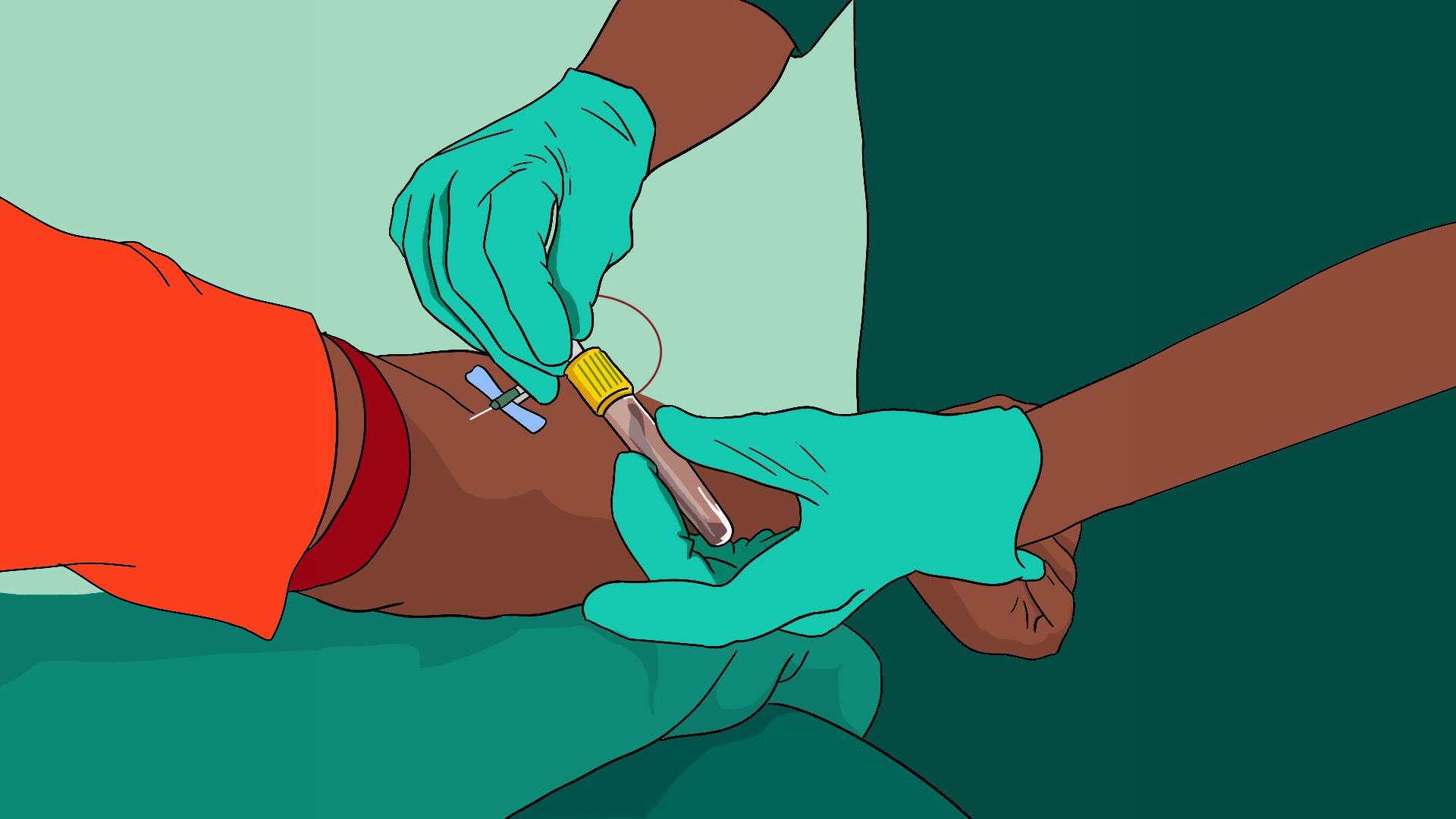
What is blood transfusion?
A blood transfusion is when a person receives blood through a small tube inserted into their vein (intravenous or IV line). This can be done for different reasons:
- After a serious injury or surgery: If someone loses a lot of blood, they need an urgent transfusion to stay alive.
- For medical conditions: People with diseases like sickle cell anaemia, severe infections, liver disease, or cancer may need regular blood transfusions (transfusion therapy) to stay healthy.
Before any transfusion, donated blood is tested to make sure it is safe and matches the recipient’s blood type.
How common is blood transfusion in Africa?
- Maternal health: In sub-Saharan Africa, over 200,000 women die each year from pregnancy-related bleeding. Many of these deaths could be prevented with timely blood transfusions.
- Sickle cell disease: Around 1,000 babies are born with sickle cell disease every day in Africa, and many of them need frequent blood transfusions to survive.
- Accidents & trauma: Road accidents are a major cause of death in Africa. Many victims need urgent blood transfusions, but hospitals often run out of blood.
- Malaria & anaemia: Severe malaria can cause extreme blood loss, especially in children under five, who may require emergency transfusions.
Understanding blood types?
Your blood type is determined by special markers in your blood called antigens. The four main blood groups are:
- O
- A
- B
- AB
Some people also have a special protein in their blood called the Rh factor. If you have it, you are Rh positive (+); if you don’t, you are Rh negative (-). For example, someone might have O+ or B- blood type.
Knowing your blood type is important because only certain types of blood can be given to you safely.
Are there risks in blood transfusion?
Blood transfusion is generally safe, but like any medical procedure, there can be side effects. Some people might experience:
- Mild symptoms: Chills, fever, headache, or muscle pain.
- Delayed reaction: Some people develop reactions weeks after the transfusion.
- Rare but serious reactions: If the blood type is not a perfect match, the immune system might attack the new blood.
Fortunately, hospitals test donated blood carefully to reduce these risks.
Are there alternatives to blood transfusion?
There are no complete substitutes for human blood, but some methods can help reduce the need for transfusion:
- Medicines like erythropoietin help the body produce more red blood cells.
- Autotransfusion: In some surgeries, doctors collect and reuse a patient’s lost blood instead of using donated blood.
However, when someone desperately needs blood, a transfusion is the only way to save their life.
Blood donation?
Blood donation means giving a small amount of your blood to help someone in need. You never know when you or a loved one might need it!
Who Can Donate Blood?
To donate blood, you need to:
- Be between 17 and 60 years old
- Weigh at least 50kg
- Be in good health
- Have enough blood to give (Haemoglobin 12g/dl or above)
- Have normal blood pressure Who cannot donate blood?
Some people cannot donate blood for health reasons. You may not be allowed to donate if you:
- Have kidney or heart failure
- Use illegal drugs
- Have sickle cell disease (SS, SC, SE)
- Have severe diabetes complications or take insulin
- Have tested positive for HIV, Hepatitis B, or Hepatitis C
- Have had a recent tattoo or piercing
If you are temporarily disqualified, doctors will advise you on when you can return to donate.
Common myths about blood donation & transfusion?
- “Blood donation is painful.” The only pain is a small needle prick. The rest is painless.
- “Donating blood makes you weak.” Your body quickly replaces the donated blood within days.
- “Blood donation takes too long.” The process takes about 25 minutes, and you’re done within an hour.
- “I donated once, so I’m done.” Men can donate every 3 months; women every 4 months. Up to 3 donations a year are allowed.
- “Blood donation is compulsory.” In Ghana, every pregnant woman must have someone donate blood in her name, ensuring there is always blood available in hospitals.
Conclusion: Why blood donation matters in Africa? Many lives are lost daily in Africa due to a lack of blood. Pregnant women, accident victims, children with malaria, and sickle cell patients all depend on blood donors to survive.
