🎧 Listen to: Bug Bites
Bug Bites
Introduction: Why you should care about bug bites
In Africa, bug bites are more than just a minor annoyance. Many insects carry diseases that can be life-threatening. For example, mosquitoes are responsible for spreading malaria, which affects millions of Africans each year. In 2021 alone, Africa accounted for 95% of global malaria cases and 96% of malaria deaths. Other bug bites can cause serious allergic reactions or infections.
Understanding the dangers of bug bites and knowing how to prevent and treat them can protect you and your loved ones from serious health problems.
What are bug bites?
Bug bites happen when insects or arachnids (such as spiders, ticks, and scorpions) bite or sting a person. While most bites cause minor swelling and itching, some can lead to severe allergic reactions or transmit dangerous diseases.
Why should you be concerned?
- Some insect bites transmit diseases like malaria, yellow fever, and sleeping sickness.
- Some people may have severe allergic reactions to bug bites, leading to breathing difficulties and other complications.
- Certain insect stings, such as from scorpions or some spiders, can be lifethreatening if not treated quickly.
How common are bug bites in Africa?
Bug bites are very common across the continent due to the warm climate, which favors insect breeding. Some examples include:
- Mosquito bites: Cause malaria, dengue fever, and yellow fever.
- Tsetse fly bites: Spread sleeping sickness (trypanosomiasis), which is fatal if untreated.
- Scorpion stings: More common in desert and dry areas, leading to intense pain and possible poisoning.
- Tick bites: Can transmit tick-borne diseases like Lyme disease and African tick-bite fever.
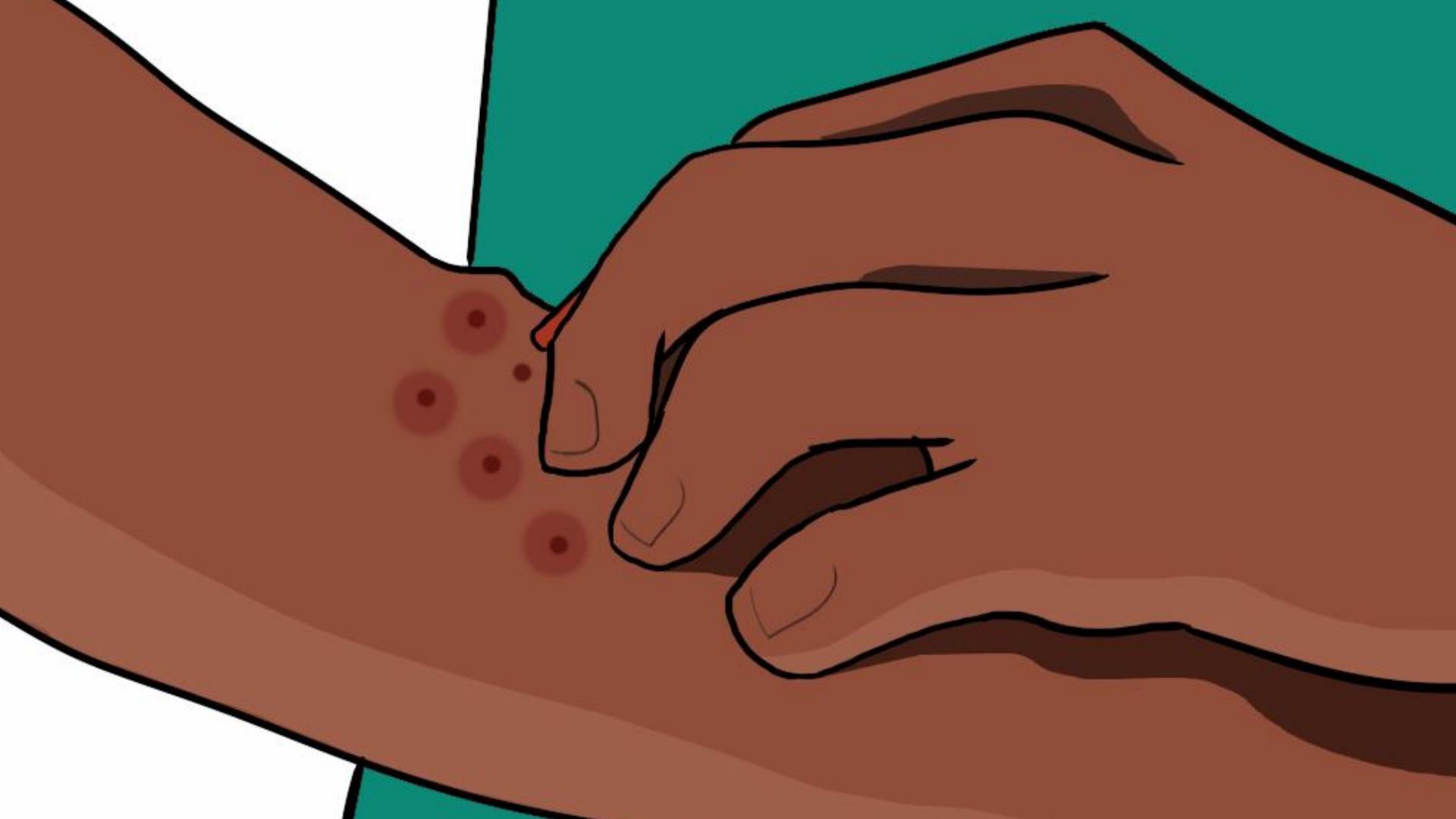
Common bug bites and their symptoms?
Each type of bug bite has different symptoms and risks. Below are the most common ones:
Mosquito bites
- Appear as small, round, itchy bumps.
- Can transmit malaria, yellow fever, and dengue fever.
- Often worsen at night.
Fire ant bites (locally known as kakape in some African regions)
- Appear as red, swollen spots that develop blisters.
- Cause intense burning and itching.
- Can last up to a week.
Bedbug bites
- Often found on areas of skin not covered by clothes.
- Cause itchy, red rashes in clusters.
- Can lead to secondary skin infections from scratching.
Bee and wasp stings
- Cause immediate pain, redness, swelling, and itching.
- Wasp stings may cause larger, more painful swellings.
- Can trigger severe allergic reactions in some people.
Scorpion stings •
Cause intense pain, swelling, and numbness.
- In severe cases, can lead to breathing problems, muscle twitching, sweating, vomiting, and increased heart rate.
- Children are more vulnerable to severe reactions.
How to treat bug bites?
If you or someone around you gets bitten, here’s what to do:
- Remove the stinger if it’s lodged in the skin (for bees or wasps).
- Wash the affected area with soap and water.
- Apply an ice pack to reduce swelling and pain.
- Use a thin paste of baking soda to relieve itching.
- Take antihistamines to reduce allergic reactions (if needed).
- Seek medical attention immediately if you experience severe symptoms like difficulty breathing, excessive swelling, or dizziness.
When to see a doctor?
- If the bite or sting causes severe swelling or difficulty breathing.
- If the wound becomes infected (red, warm, pus-filled, or increasingly painful).
- If bitten by a venomous insect, such as a scorpion.
How to prevent bug bites?
Prevention is always better than cure. Here’s how to protect yourself:
- Use insect repellent when outdoors, especially at night.
- Sleep under treated mosquito nets to prevent malaria.
- Wear long sleeves and trousers in high-risk areas.
- Keep your environment clean to prevent breeding of insects like mosquitoes and bedbugs.
- Avoid strong perfumes and scented lotions, which attract bugs.
Conclusion?
Bug bites may seem like a minor inconvenience, but in Africa, they can pose serious health risks. Knowing how to identify, treat, and prevent bug bites can protect you and your family from infections, allergic reactions, and deadly diseases. If you experience severe symptoms after a bite, seek medical attention immediately.
